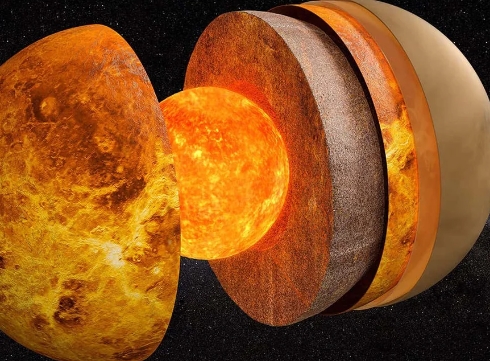
Venus, the second planet from the sun, is often referred to as Earth’s “sister planet” due to its similar size and composition. But there is more to Venus than meets the eye. Unlocking the secrets of Venus’ mystical shape reveals fascinating insights into the nature of this enigmatic planet.
Mysterious Atmosphere
Venus is shrouded in a thick layer of clouds composed mainly of sulfuric acid, which reflects sunlight and gives the planet its bright appearance. This dense atmosphere creates a greenhouse effect, trapping heat and making Venus the hottest planet in our solar system.
Rotational Mystery
Venus rotates on its axis in the opposite direction to most planets, a phenomenon known as retrograde rotation. This slow, retrograde rotation causes the sun to rise in the west and set in the east on Venus, creating long days and nights on the planet.
Volcanic Activity
Venus is home to thousands of volcanoes, many of which are still active. These volcanoes have shaped the planet’s surface, creating vast lava plains and towering mountain ranges. The intense heat and pressure on Venus cause frequent volcanic eruptions, releasing gases into the atmosphere.
Geological Features
The surface of Venus is marked by a variety of geological features, including impact craters, mountain ranges, and vast plains. The planet’s terrain is constantly changing due to tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions, creating a dynamic landscape unlike any other in our solar system.
Magnetic Field
Despite its similarities to Earth, Venus has a much weaker magnetic field. This lack of a strong magnetic field allows solar wind to strip away Venus’ atmosphere, causing the planet to lose its water and other volatile compounds over time.
Understanding the mysteries of Venus’ shape and composition can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. By studying this enigmatic planet, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of Earth’s own history and potential future. Unlocking the secrets of Venus is a tantalizing challenge that continues to captivate astronomers and space enthusiasts around the world.