The Mantle: A Key Component of Earth’s Structure
The mantle is a layer of Earth located between the crust and the core. It plays a crucial role in various Earth processes and has a significant impact on the planet’s overall dynamics.
Understanding the Composition of the Mantle
The mantle is primarily composed of silicate minerals, with the most abundant being olivine and pyroxene. These minerals give the mantle its unique properties and help regulate Earth’s internal heat flow.
The Mantle’s Role in Plate Tectonics
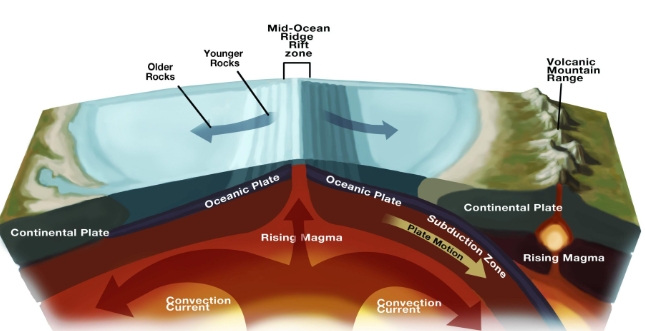
The mantle is directly involved in the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates. Convection currents within the mantle drive plate movements, leading to processes such as seafloor spreading, subduction, and mountain formation.
Seismic Waves and the Mantle
Scientists study seismic waves to learn more about the mantle’s composition and structure. Different types of waves travel through the mantle at varying speeds, providing valuable insights into its density and temperature distribution.
The Importance of Mantle Plumes
Mantle plumes are hot, buoyant upwellings of material within the mantle. These plumes can cause volcanic activity and the formation of hotspots, such as the one responsible for the Hawaiian Islands.
The Mantle’s Influence on Earth’s Surface
The mantle’s movements and processes have a direct impact on Earth’s surface features. From earthquakes to volcanic eruptions, the mantle plays a crucial role in shaping the planet’s landscape and geology.
In conclusion, the mantle is a key component of Earth’s structure and dynamics. Its composition, movements, and interactions with other layers of the planet contribute to the complex processes that drive the evolution of our planet. Understanding the significance of the mantle is essential for Earth scientists to unravel the mysteries of our dynamic planet.