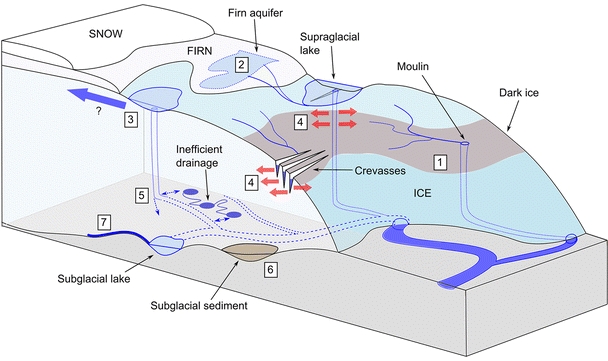
Understanding the secrets of Moulin Geomorphology
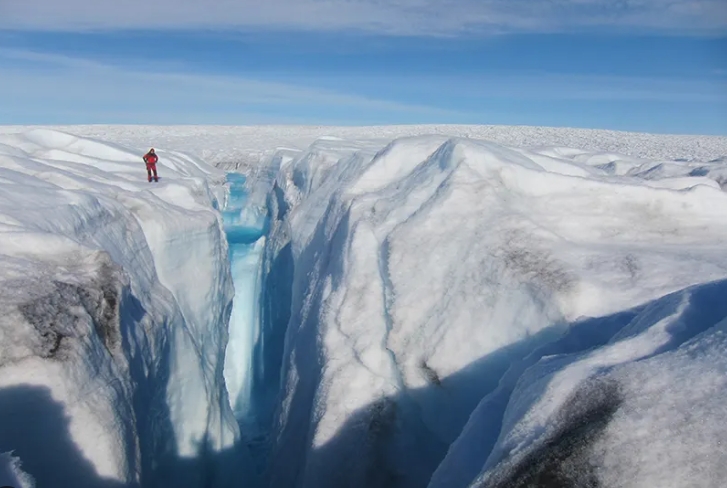
Moulin geomorphology is a fascinating field that aims to unravel the mysteries of these enigmatic landforms. Moulins are vertical shafts that form on the surface of glaciers, allowing meltwater to flow from the glacier surface to its base.
Formation process of Moulins
Moulins are typically formed through a combination of factors such as melting snow and ice, frictional heating, and the presence of pre-existing fractures in the glacier. As meltwater accumulates on the glacier surface, it seeks out weak points in the ice, eventually carving out a vertical shaft that can extend hundreds of feet deep.
Role of Moulins in glacier dynamics
Moulins play a crucial role in the dynamics of glaciers by allowing meltwater to penetrate deep into the glacier, lubricating its base and promoting faster movement. This can lead to increased melting, calving, and ultimately, glacier retreat.
Research challenges in studying Moulins
Studying Moulins poses several challenges due to their remote locations and the harsh conditions in which they form. Researchers often face difficulties in accessing moulins, collecting data, and monitoring changes over time.
Implications for climate change
Understanding the processes that govern moulin geomorphology is crucial for predicting the impacts of climate change on glacier dynamics. As temperatures rise and glaciers continue to recede, moulins may play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of our planet.
Conclusion
Uncovering the mysteries of moulin geomorphology is an ongoing and dynamic field of research that offers valuable insights into the complex interactions between glaciers, meltwater, and climate change. By studying moulins, scientists can gain a better understanding of how these enigmatic landforms shape our world and inform strategies for mitigating the effects of global warming.