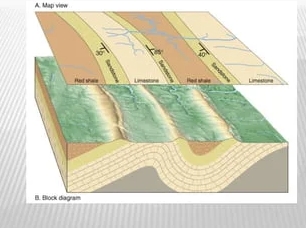
Structural geomorphology is the study of how the Earth’s surface is shaped by tectonic forces and geological structures. This field of study helps us understand why certain landforms exist and how they are connected to the underlying geology. By uncovering the hidden forces that shape the Earth’s surface, scientists can gain valuable insights into the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
Understanding Geological Structures
Geological structures such as faults, folds, and fractures play a key role in shaping the Earth’s surface. Faults are fractures in the Earth’s crust where rocks on either side have moved relative to each other. Folds are bends or curves in rock layers caused by tectonic forces. Fractures are cracks in the Earth’s crust that allow rocks to break and shift.
Interpreting Landforms
By studying the distribution and orientation of geological structures, scientists can interpret how different landforms have been shaped. For example, a series of parallel fault lines may be responsible for the formation of a mountain range. A network of fractures may create a pattern of interconnected valleys. By analyzing these patterns, researchers can unravel the hidden forces that have shaped the Earth’s surface.
Mapping Tectonic Activity
Structural geomorphology also helps us map areas of active tectonic activity. By identifying faults and folds in the Earth’s crust, scientists can pinpoint regions where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are likely to occur. This information is crucial for assessing the seismic hazards in a particular area and planning for disaster management.
Predicting Future Landforms
By studying how geological structures have shaped the Earth’s surface in the past, scientists can make predictions about future landforms. For example, if a fault is currently active and causing the uplift of a mountain range, we can expect to see further changes in the landscape over time. By understanding the underlying geological processes, we can anticipate how the Earth’s surface will evolve in the future.
In conclusion, structural geomorphology is a valuable tool for uncovering the hidden forces that shape the Earth’s surface. By studying geological structures, interpreting landforms, mapping tectonic activity, and predicting future landforms, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the Earth’s past, present, and future, and for managing geological hazards in a proactive manner.