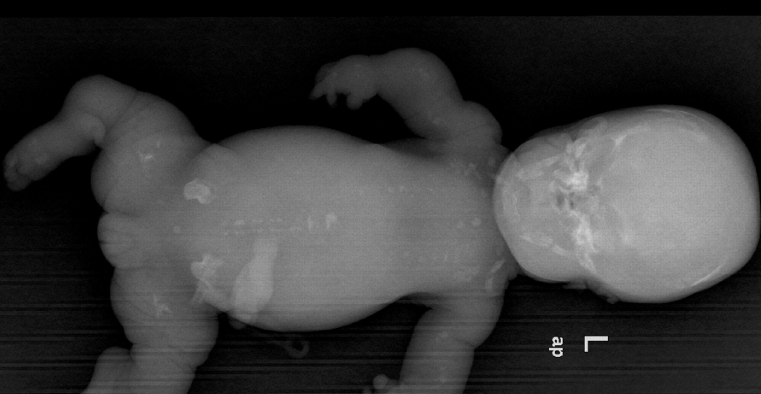
Diastrophic dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and joints in the body.
Understanding Diastrophic Dysplasia:
Diastrophic dysplasia is caused by mutations in the SLC26A2 gene on chromosome 5.
This gene provides instructions for producing a protein called sulfate transporter.
The sulfate transporter is essential for the formation of cartilage and the development of bones and joints.
Role of Chromosome 5:
Chromosome 5 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human genome.
It contains approximately 923 genes, including the SLC26A2 gene implicated in diastrophic dysplasia.
Mutations in the SLC26A2 gene on chromosome 5 disrupt the normal function of the sulfate transporter protein, leading to the characteristic features of diastrophic dysplasia.
Symptoms of Diastrophic Dysplasia:
People with diastrophic dysplasia may have a variety of symptoms, including short stature, joint deformities, and abnormal curvature of the spine.
They may also experience hearing loss, breathing difficulties, and problems with their vision.
Individuals with diastrophic dysplasia may require ongoing medical care to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Treatment and Management:
Treatment for diastrophic dysplasia typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including orthopedic care, physical therapy, and medical interventions to address specific symptoms.
Surgical interventions may be necessary to correct joint deformities and improve mobility.
Early diagnosis and intervention can help improve outcomes for individuals with diastrophic dysplasia.
In conclusion, understanding the role of chromosome 5 and the SLC26A2 gene is crucial for identifying and managing diastrophic dysplasia. Ongoing research into the genetic mechanisms underlying this disorder may lead to new treatment options and improved outcomes for affected individuals.